Google Knowledge Graph: Definition, Algorithm Updates and How It Works

What is Google’s Knowledge Graph?
Google’s Knowledge Graph is Google’s machine-readable encyclopedia that stores the “facts” the search engine understands about the world. Google’s algorithms collect and verify facts from various sources on the Internet to populate the Knowledge Graph with Entities. Entities are “things or concepts” identifiable and definable, such as people, places, podcasts, music groups, or events.
Google introduced the Knowledge Graph in 2012 to shift from matching keywords to keywords to providing real-world search results based on its understanding of the world through Entities and their attributes, such as date of birth and location and their relationships with other Entities.
The Knowledge Graph improves Google’s search results by understanding the semantic relationships and context between entities, attributes, and relationships to understand the meaning behind the words a user types into the Google search bar. The aim of Google’s Knowledge Graph is to provide users with information that is most relevant to their search by understanding the user’s context and intent.
Entities in the Knowledge Graph have a Universal Resource Identifier or KGID and a Knowledge Panel. Knowledge Panels are not automatically displayed for a search for an Entity until the Google Algorithms are confident in understanding the facts about an Entity.
Google has six Knowledge Graphs verticals: Google Maps, Google Books, Google Scholar, Google Podcasts, the main web index, and the main Knowledge Graph. Kalicube calls the Main Knowledge Graph the Knowledge Vault. The Knowledge Graph verticals are Google’s way of consolidating different knowledge areas into a universal understanding for machines. The Main Knowledge Graph or Knowledge Vault houses information Google’s algorithms have verified as “Facts.”
Google’s Knowledge Vault contains 1,500 billion facts and was originally filled with information curated by Google Engineers but is now populated algorithmically. Once Google is confident of its knowledge about an Entity, it moves all the information into the Knowledge Vault so that the algorithms see it as indisputable truth.
What Information Is Included in the Knowledge Graph?
The information included in Google’s Knowledge Graph is 1,500 billion machine-readable facts.
The Knowledge Graph includes the items listed below.
- Information about entities such as people, places, and things, along with their attributes such as date of birth or location.
- Relationships between different entities, for example, who has worked for which company, who has played in which group, which company specializes in which products, who is an expert on which topic, etc.
Nobody knows exactly all the information in the Knowledge Graph because it is extensive and Google offers limited access via its Knowledge Graph API (Application Programming Interface).
Kalicube Pro™ has a free tool Knowledge Graph API Explorer, to search Google’s Knowledge Graph. Use the tool to check your brand name, business name, or other Entity. It leverages the power of Google’s Knowledge Graph API to perform a comprehensive search of the Knowledge Graph. This search shows Entities relevant to your query and covers a wide range of categories, such as brands, companies, events, products, people, and topics. The API Explorer provides insights into the amount of information available in Google’s Knowledge Graph about these Entities and the level of trust associated with this information. The results are updated in real-time, and the information is always current.
Kalicube Pro uses data from Google dating back to 2015 (and growing), contains over 50 million Knowledge Panels, tracks 7.3 million kgid, over 3 billion data points, and tracks over 100,000 entities and dozens of countries. Kalicube Pro knows which sources Google trusts to corroborate business information online - and there are over 40,000 of them.

What is Google’s Knowledge Graph Algorithm Update?
Google’s Knowledge Graph Agorithm Update refers to changes or modifications that Google makes to its Knowledge Graph Algorithm. Knowledge Graph Algorithm Updates occur regularly and range from two weeks to a month or occasionally extend up to three months.
Google’s ultimate goal is to “understand the world” by filling this Knowledge Vault with the facts about the world. The Google Knowledge Graph Algorithm Update involves adding new information, establishing new relationships, improving confidence scores, and adding new entities to the Knowledge Graph. Entities, relationships, and attributes are removed, and confidence values are reduced.
Algorithm Updates cause volatility in the Knowledge Graph. The search results change, and information in Knowledge Panels change. Knowledge Panels are often affected by the algorithmic update, with many disappearing, and new ones created. Ensuring relevant, authoritative sources consistently confirm your facts is vital.
Kalicube has been tracking Google’s Knowledge Graph through the API and Knowledge Panels since 2015. Kalicube Pro tracks Knowledge Graph updates using multiple metrics across three knowledge algorithms – the Main Algorithm (Knowledge Vault), Vertical Algorithms (podcasts, books, etc.), and Corroborative Algorithms. These updates can be tracked using tools such as Kalicube Pro™’s Knowledge Graph Sensor, which monitors the timing of updates within the Knowledge Graph. This tracking allows for better management of Knowledge Panels for clients and helps mitigate the risk associated with these updates.
Read more about Google Knowledge Algorithms here >>
How Does Kalicube Measures Knowledge Graph Changes?
Kalicube measures Knowledge Graph changes using a system that tracks the confidence score returned by the Knowledge Graph API for a dataset of over 100,000 known Entities.
Kalicube isolates the three aspects of these changes and measures them daily. Kalicube measures Knowledge Graph changes by magnitude, amplitude, and depth.
- Magnitude: How many entities have experienced an increase or decrease (reach/breadth.)
- Amplitude: How significant this change was in confidence scores of the affected entities at a micro level (scope/height).
- Depth: How many entities does the Knowledge Graph API return for a query.
The graph below is an example showing Magnitude (Volatility) in purple and Depth in red. Kalicube uses amplitude and other measurements internally as part of the paid Kalicube Pro platform.

On the other hand, the graph below illustrates the volatility of confidence scores from the years 2020 to 2023. Confidence scores are important metrics that have recently been impacted by Google’s decision to sunset from 2024. From next year, their importance as an indicator of Knowledge Graph activity and updates will therefore decrease significantly. This move by Google is similar to the earlier decision to phase out PageRank scores. We can attribute this to Google’s strategy of limiting external visibility into its internal scoring systems, as users and companies tend to obsess over these so-called “official Google scores” and Entities like Kalicube have shown that they are able to decipher these metrics and figure out how they work.

At Kalicube we have developed a proprietary KaliScore™, which we call “Brand Authority” and which uses several signals to measure
- The solidity of an entity’s position in Google’s Knowledge Graphs (since 2015)
- The breadth, level and confidence in Google’s understanding of an Entity in the Knowledge Vault (since 2020)
- NEEATT (coming in 2024 and will introduce a new dimension to Kaliscore that will further improve our ability to measure and interpret brand authority using state-of-the-art techniques)
What Is the Purpose of the Knowledge Graph Update?
The purpose of the Knowledge Graph update is to improve the accuracy and relevance of Google search results. The update includes a large set of new and labeled data that has been reviewed by a team of fact-checkers. This data is then integrated into the Knowledge Graph algorithm, which analyzes it to develop an understanding of it. The updates play a key role in helping Google understand the world similarly to humans, providing users with more accurate and relevant search results. In addition, these updates affect the visibility and appearance of businesses or websites in Google search results, so it is important that they provide accurate information for optimization.
How Does the Knowledge Graph Update Affect Search Results?
The Knowledge Graph Update has a significant impact on search results. When Google’s Knowledge Graph is updated it affects the information displayed in Knowledge Panels and the search results. Existing Knowledge Panels may be affected by the algorithmic update, resulting in many of them disappearing while new ones are created.
These changes may affect what users see when they perform a search, potentially impacting traffic to certain websites or the visibility of certain entities. The update affects the way Google understands and interprets users’ search queries, which could lead to changes in how content is prioritized in search results.
For example, the Killer Whale update, which began in July 2023 and resulted in a significant E-E-A-T update to the Knowledge Graph in September 2023, caused a massive change in the depth (i.e. the number of entities it contains) of the Google Knowledge Graph (see graph below). The unique feature of this Knowledge Graph update is that it cascaded into the August 2023 core update and potentially the October 2023 core update. The Killer Whale update increased Knowledge Panels for person entities, particularly those involved in writing and research.

How Does the Knowledge Graph Update Improve the User Experience?
The Knowledge Graph Update improves the user experience by increasing the accuracy and relevance of search results. When Google updates its Knowledge Graph, it refines its understanding of entities and their relationships, which can lead to more accurate matching of search queries with relevant information. Google understands the context and meaning behind search queries, rather than matching keywords to keywords. This means that users are more likely to find exactly what they are looking for in less time.
Knowledge Graph updates cause the creation or disappearance of Knowledge Panels. Knowledge Panels are the boxes that appear on the Google search results page and provide quick access to information about an entity searched for. These panels provide users with an overview of the most important details about an entity directly in the search results, so they don’t have to click through multiple pages.
Jason Barnard has been optimizing websites for search engines since 1998 and has been tracking Knowledge Graph updates using Kalicube Pro, explains that understanding how different Knowledge algorithms work is crucial in managing Knowledge Panels effectively for clients. These algorithms are part of Google’s system to organize and present information about entities (like businesses or individuals) in its search results. By monitoring these updates, businesses can better manage their online presence and mitigate risks associated with incorrect or outdated information appearing on their Knowledge Panels. If an entity is correctly represented according to these updates, it can benefit from improved visibility and accuracy in Google’s search results.
How Often Does Google Update the Knowledge Graph?
Google updates the Knowledge Graph with a consistent regularity. These updates typically transpire every 2 to 3 weeks, although there can be extended intervals of inactivity, as illustrated below.

Will My Website’s Position on the SERP Be Affected Whenever There Is a Google Knowledge Graph Update
Yes, your website’s position on the Search Engine Results Page (SERP) is affected by any update to the Google Knowledge Graph. Updates to entities, attributes and relationships produce changes in the search results and the information displayed in the Knowledge Panels.
The impact of these updates is positive or negative. A positive impact mean that your Brand SERP improves and your website appears in SERPs where your brand name is not directly searched for. This gives you additional visibility to highly relevant audiences in all Google search results and likely a visible presence in your competitors’ Brand SERPs.
Negative impact means a less desirable Brand SERP, the loss of your Knowledge Panel attributes, or the loss of your Knowledge Panel itself. From a Brand SERP perspective, this is disastrous as you would have lost a large portion of SERP real estate as well as Google’s seal of approval and credibility in the eyes of your target audience.
Kalicube actively checks every single Google Knowledge Algorithm update. The Kalicube Pro platform’s process is fully aligned with the goals of these algorithms. It tracks and measures these updates against multiple metrics that allow us to better manage Knowledge panels for our clients and mitigate risk for them.
How Can I Optimize My Website for the Knowledge Graph Update?
To optimize your website for the Knowledge Graph update, follow these four strategies.
Identify Your Entity Home
Identify your Entity Home, which is a website page recognized by Google as the authoritative source for factual information about a given entity. This could be a brand, company, person, product, podcast, music group, etc. The Entity Home is where the entity “lives” online and serves as a reference point for Google and other companies building large-scale knowledge graphs such as Bing, Amazon, Microsoft, Facebook, and Apple. The Entity Home must be a page on your website where you describe who you are, what you do, and who your audience is in clear simple terms, such as the “About Us” page.
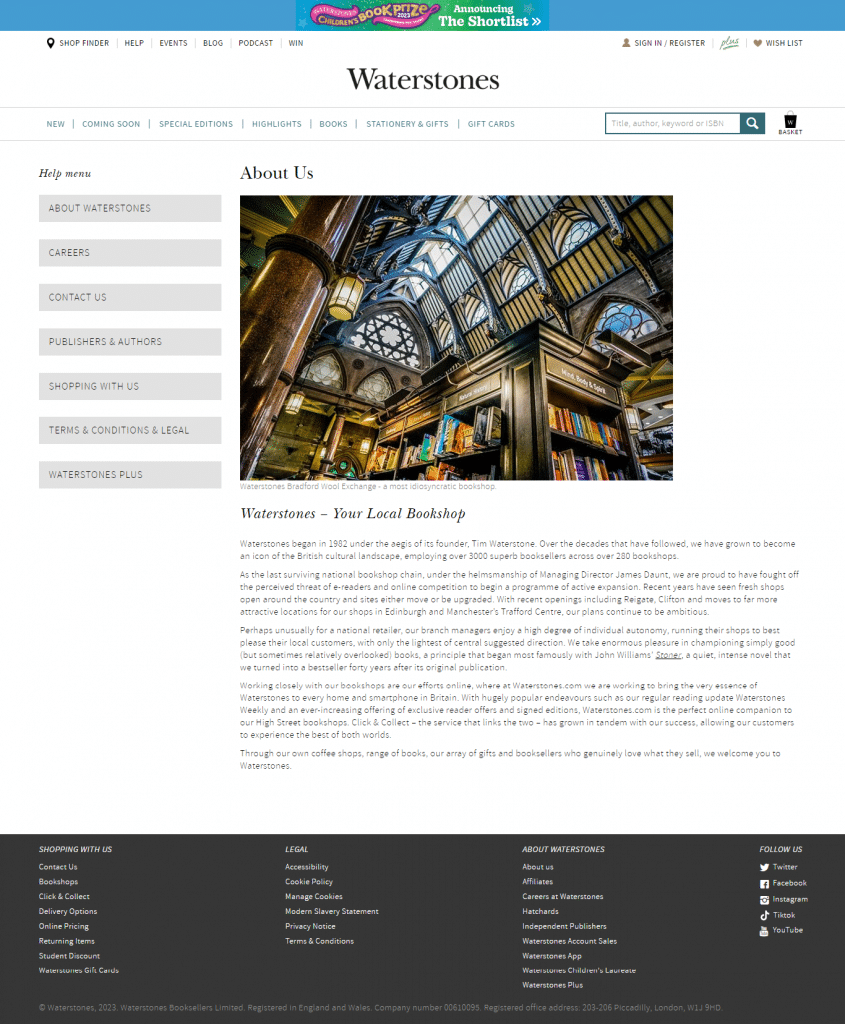
Communicate clearly to Google who you are
Communicate your company or brand’s identity and offerings to Google in a clear and unambiguous manner by providing explicit content that accurately represents who you are, what you do, and who your target audience is.
Pay attention to your published content. Copywriting plays an essential role in this process, as well-crafted content weaves meaning into the entity. Meaning and context help build Google’s confidence in its understanding of your brand - giving you an advantage in a digital marketing strategy.
Being clear about who you are and what you offer on every platform that talks about you ensures getting into Google’s Knowledge Graph, which triggers a Knowledge Panel on Google for search queries related to your brand or personal name. This positions you ahead of the competition by demonstrating credibility through consistent messaging across various platforms thereby optimizing your online presence.
Structure your content
Use Schema.org markup, HTML tables, HTML5 headings, sections etc., to give your content an explicit structure. This helps the Knowledge Extraction Algorithm understand the role each piece of content on a page plays and attributes a high confidence score to important information about the entity.

Provide reliable and authoritative corroboration
Provide Google with social proof and consistent signals that allow it to have more confidence in its understanding of your entity. The more corroborative evidence there is supporting what you claim about yourself on different platforms (your website, social media pages, and particularly third-party sites etc.), the more confidence Google has in its understanding of what you represent as a brand/entity. When Google has high confidence in its understanding of an entity due to corroborative information from various sources confirming that entity’s claims about itself – it promote that entity more prominently on SERPs.
Can I Influence What Information Is Displayed in the Knowledge Graph for My Website?
Yes, you can influence what information is displayed in the Knowledge Graph for your website by educating Google’s algorithms about your brand. Educating Google requires consistency across every platform you control. Create an Entity Home on your website with all relevant information about your brand. Over time, Google’s algorithms will develop an understanding of your brand and be confident about your facts.
Maintain up-to-date and consistent information across all your web assets. This applies not only to your own website but second and third party websites where your brand has a presence. The content you create should consistently emphasize your brand’s message, values, services, or products. Gathering reviews from trusted third-party websites can significantly increase the credibility of your data. These reviews validate what you claim about your entity and can help build trust with potential customers and search engines like Google.
However, it’s important to note that while you can directly or indirectly suggest changes to the Knowledge Panel, Google’s Knowledge Graph verticals have ultimate control over what information appears in a Knowledge Panel. The changes made should not contradict most of the information available on the web, in which case Google’s machine may override the changes made.
How Does the Knowledge Graph Update Affect SEO Strategies?
The Knowledge Graph update has a significant impact on SEO strategies because Google is moving to “things not strings”, or entity-based, semantic search. Google must verify the facts about the entities in its Knowledge Graph to make this shift.
The Killer Whale Update clearly reclassified the subtitles in Knowledge Panels to Writer/Author. Google’s algorithms are able to apply EEAT signals to writers. EEAT is Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. Topic layers and entities mean moving beyond traditional link-based strategies and embracing broader credibility indicators such as your qualifications, company awards, user reviews, social media mentions, conference participation, and article publication.
This presents a unique opportunity for content creators. Writers, video producers, or podcasters are able to demonstrate EEAT signals Google is able to apply to their entity. EEAT is a cornerstone in SEO strategy, positioning entities at the very heart of it.
Whether you are a person or company, focus on educating Google about who you are, what you do, who your target audience is, and why you’re a great solution to your audience. Present a complete and accurate picture of your entity as a whole so that Google is able to reconcile the scattered information about your entity it finds on the web.
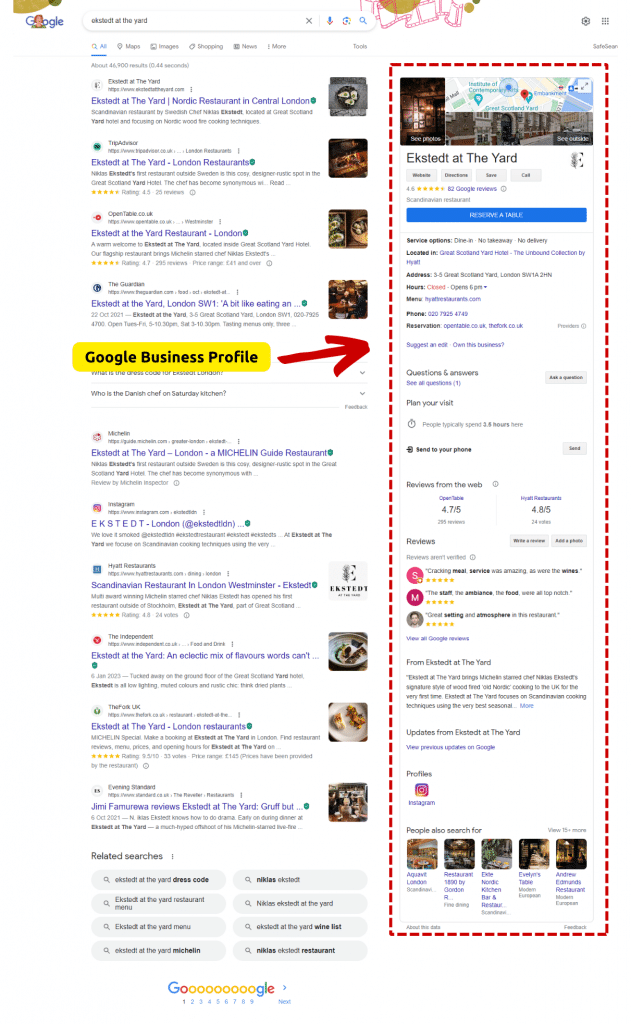
For example, if you are a local business, you need to optimize your use of Google Business Profile, which are populated with information from the Knowledge Graph. However, it is important that you provide accurate information and get a handle on fake feedback that can distort the “facts” about you.
As the Knowledge Graph becomes deeper with the updates (returning more entities per search query), SEO must shift from focusing on websites to building a web source. A web source is a topical authority about your brand, which is consistently portrayed across the entire digital ecosystem. SEO is about packaging your brand and marketing efforts online in a way machines can understand them.
How Does the Knowledge Graph Update Affect Google’s Ranking Algorithm?
The Knowledge Graph update affects Google’s ranking algorithm by changing the visibility and presentation of entities within the SERP. Google is integrating more and more entities into the SERP, especially in the left rail, as part of its algorithmic processes. This includes not only the traditional blue links, but entity boxes, related searches, people also ask, image boxes, and even the suggestions that appear in the drop-down menu when you type a query into the search bar. Entity-related features are foundational to the Google search experience and originate from Knowledge Graph data.
When Google updates the Knowledge Graph, the Entities on the Left Rail, including attributes and confidence scores, will be affected, impacting what information appears in search results and how it is displayed.
For example, if an entity’s confidence score increases because it is frequently mentioned or is currently in the news, that entity may be highlighted more prominently in the SERPs. Conversely, entities with lower scores or less relevance may lose visibility.
Furthermore, as Google aims to provide relevant and accurate information to users quickly and efficiently through the Knowledge Panels, and the information in these panels is derived from the Knowledge Graph, updates to the system could lead to shifts in ranking as Google rebalances the information it deems most authoritative or relevant for a particular search query.
How Does the Knowledge Graph Update Affect Google’s Artificial Intelligence?
The Knowledge Graph has a significant impact on Google’s AI algorithms, especially as these algorithms are instrumental in updating the Knowledge Graph by transforming unstructured web information into structured data. Artificial intelligence represents an advanced level at which machines exhibit intelligent behavior on their own.
AI algorithms demonstrate Google’s growing confidence in its ability to analyze text and extract factual information from unstructured sources. Google has moved away from its heavy reliance on Wikipedia, indicating Google now trusts its Natural Language Processing (NLP) algorithms to a high degree. Google has reduced its reliance on Wikipedia as a trusted source because the facts in the Knowledge Graph have outgrown the articles on Wikipedia. Google has given AI more autonomy in decision-making.
AI now has even greater control than before. For example, if an error occurs in the Knowledge Graph or your Knowledge Panel, you can still ask a human employee from Google to make the corrections. The algorithm has the final say; it determines what stays and what disappears. If the algorithm thinks the change you requested is wrong, it will revert it. This means that you need to understand why the algorithm thinks something is wrong, and you need to address that specific misinformation so that the algorithm can learn from it. Every company or person must ensure that information is consistent across all online platforms - not just their own website.
How Does the Knowledge Graph Fit Into Brand SERP Optimisation and Knowledge Panel Management?
Google’s Knowledge Graph plays a crucial role in SEO. It represents Google’s comprehensive understanding of the world and significantly influences the search results it generates. This includes Brand SERPs (the results displayed when your brand name is searched for), information searches related to your brand, and generic queries such as “best noise-cancelling headphones”
Inclusion in Google’s Knowledge Graph is a great benefit for your brand’s visibility. When your brand is included in the Knowledge Graph, Google is more likely to present your brand positively, accurately, and persuasively in search results. This includes displaying a Knowledge Panel, which appears on the right-hand side of desktop search results and provides accurate and helpful facts about your brand.
Inclusion in Google’s Knowledge Graph is a “stamp of approval” from Google This presence not only boosts the positivity, accuracy, and persuasiveness of your Brand SERP but lends a level of credibility and recognition that can be extremely valuable for digital marketing and brand representation.
Do you have a question? Book a call with Jason Barnard today.